Convective instability — For a more general discussion of the same phenomenon, see Convective available potential energy. This article incorporates public domain text created by the US government. In meteorology, convective instability or stability of an airmass refers… … Wikipedia
Convective available potential energy — A skew T plot showing a morning sounding with a large hydrolapse followed by an afternoon sounding showing the cooling which occurred in the mid levels resulting in an unstable atmosphere as surface parcels have now become negatively buoyant. The … Wikipedia
Instability — [ Hydrodynamics simulation of the Rayleigh–Taylor instability [Shengtai Li, Hui Li Parallel AMR Code for Compressible MHD or HD Equations (Los Alamos National Laboratory) [http://math.lanl.gov/Research/Highlights/amrmhd.shtml] ] ] Instability in… … Wikipedia
Convective inhibition — A Skew T diagram with important features labeled Convective inhibition (CIN or CINH) is a numerical measure in meteorology that indicates the amount of energy that will prevent an air parcel from rising from the surface to the level of free… … Wikipedia
Convective condensation level — The convective condensation level (CCL) represents the height where an air parcel becomes saturated when lifted adiabatically to achieve buoyant ascent. It marks where cloud base begins when air is heated from below to the convective temperature … Wikipedia
Convective temperature — The convective temperature (CT or Tc) is the approximate temperature that air near the surface must reach for cloud formation without mechanical lift. In such case, cloud base begins at the convective condensation level (CCL), whilst with… … Wikipedia
Convective overturn — The convective overturn model of supernovae was proposed by Bethe and Wilson in 1985, and received a dramatic test with SN 1987A, and the detection of neutrinos from the explosion. The model is for type II supernovae, which take place in stars… … Wikipedia
instability line — Meteorol. a nonfrontal line of convective activity in the atmosphere, usually several hundred miles long but of relatively brief duration. * * * … Universalium
instability line — Meteorol. a nonfrontal line of convective activity in the atmosphere, usually several hundred miles long but of relatively brief duration … Useful english dictionary
Horizontal convective rolls — producing cloud streets (lower left portion of the image) over the Bering Sea … Wikipedia
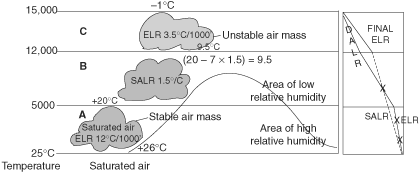 A parcel of air is stable at A and B and becomes unstable at C indicating convective instability from C onwards.
A parcel of air is stable at A and B and becomes unstable at C indicating convective instability from C onwards.